What is Blockchain and how does Blockchain technology work?
Blockchain technology or chain of blocks is one of the most innovative and disruptive concepts of recent years. However, sometimes it is difficult to understand what is a blockchain? What differentiates it from cryptocurrencies? How does Blockchain work? What advantages does it have? How does a node work in the network? . Do not worry because we have prepared this complete guide on what Blockchain is and how this technology works so that you do not have any doubts. Let’s start!
If we analyze Google Trends, we will see that searches for the term “blockchain” have been increasing since 2013, thus representing that it is a trend that is stabilizing and in the process of maturing.
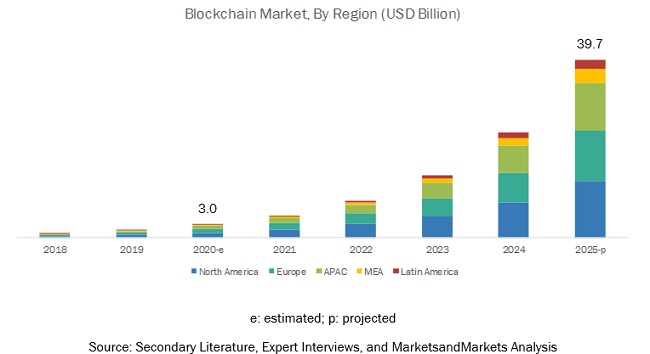
And it is that according to the report published by MarketsandMarkets this 2022, the global blockchain or block chain market is expected to grow from 5 billion dollars in 2020 to almost 40 billion in 2025. This represents a compound annual growth of 67% year after year until 2025.
Blockchain is the technology behind Bitcoin and allows you to eliminate intermediaries and store transactions safely. For this reason, large companies and banks (and some startups as well) are already exploring its possibilities. Do you want to know what this innovative technology consists of?
What is Blockchain or chain of blocks?
Blockchain is a technology based on a chain of decentralized and public operations blocks. This technology generates a shared database to which its participants have access, who can track each transaction they have made. It is like a large, unchangeable and shared ledger that is written by a large number of computers simultaneously.
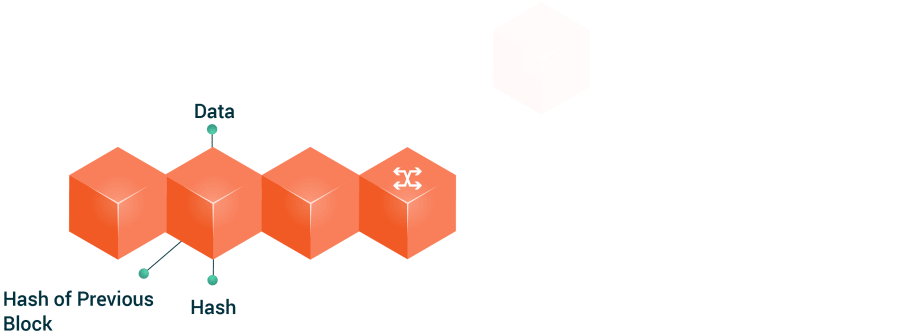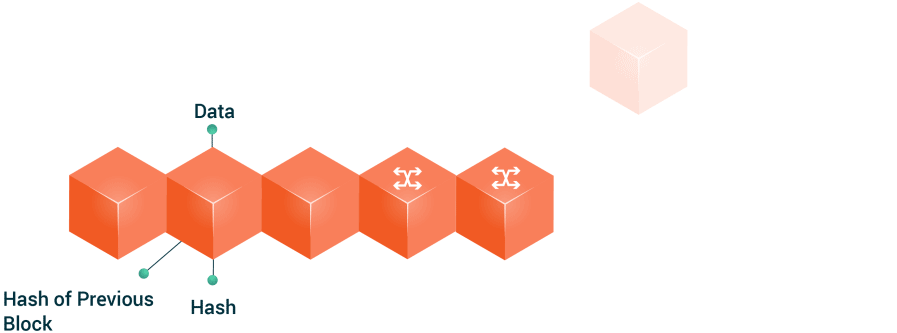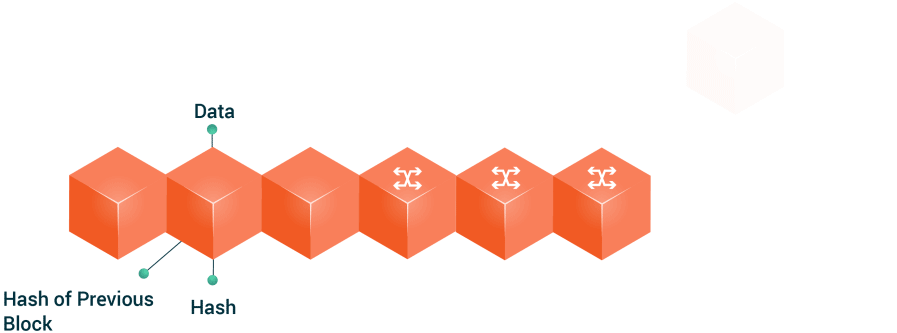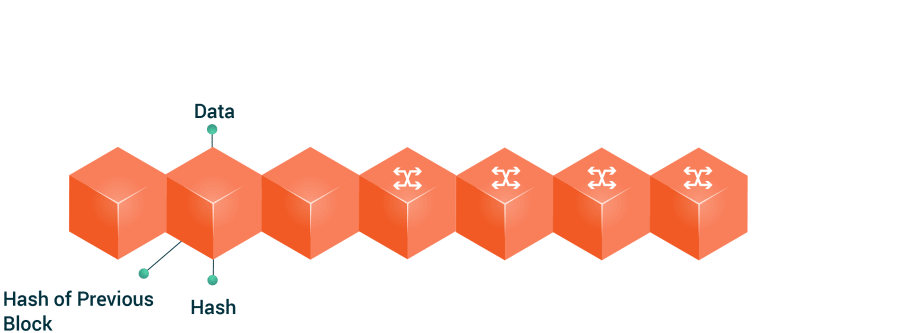
Every time a member of the network performs a digital transaction, said transaction generates associated data that will be stored in one of the blocks. When that block is full of information, the block is coupled to the already existing block chain or blockchain.
The information that is stored on said network will depend on the purpose for which it was created. It can be a network that stores payment data (cryptographic currency or cryptocurrencies), medical information, logistics or food traceability data and even electoral data count.
The difference between blockchain and a centralized network (a traditional server that stores data) is that the blockchain network runs on multiple computers distributed around the world and not in a single site. This makes the blockchain network present a series of advantages such as privacy, decentralization or not depending on a centralized executor or security . However, it presents a series of challenges that we will assess later in the section on advantages and disadvantages.
The programmable and open nature of this technology allows innovating the financial sector and administrative processes to make them more efficient and transparent. In addition, the bureaucracy is reduced. The Blockchain is the technology that developed Bitcoin , the virtual and intangible cryptocurrency that is supported by the P2P protocol and network.
In short, with Blockchain, processes are streamlined and cheaper, transactions are more transparent and intermediaries are eliminated.
How does Blockchain Technology work?
The blockchain is a record of all transactions, stored and shared publicly. The so-called miners are responsible for verifying these transactions. After that, they are included in the chain and distributed to the nodes that make up the network.
Let’s see what each of these elements consists of:
1# Blocks
A block is made up of a set of transactions. Each one is part of the blockchain. The Bit2me company, specialized in Bitcoin and its technology, defines each of the parts that make up a block:
* An **alphanumeric code** that links to the previous block.
* The “**package**” of transactions that it includes (the number of which is determined by different factors).
* Another **alphanumeric code** that will link to the next block.
What the next block in progress is trying to do is find out with calculations the alphanumeric code that allowed the previous block to link to this one.
2# Miners
Miners are computers/chips that are responsible for verifying all transactions. When someone completes a block or makes a transaction, they receive a reward in the form of Bitcoins.
3# Nodes
A node is a computer/chip that is connected to the Bitcoin network. It is dedicated to storing and distributing an up-to-date copy of the blockchain. Therefore, each new block that is confirmed is added to the chain of blocks and to the copy that each node stores.
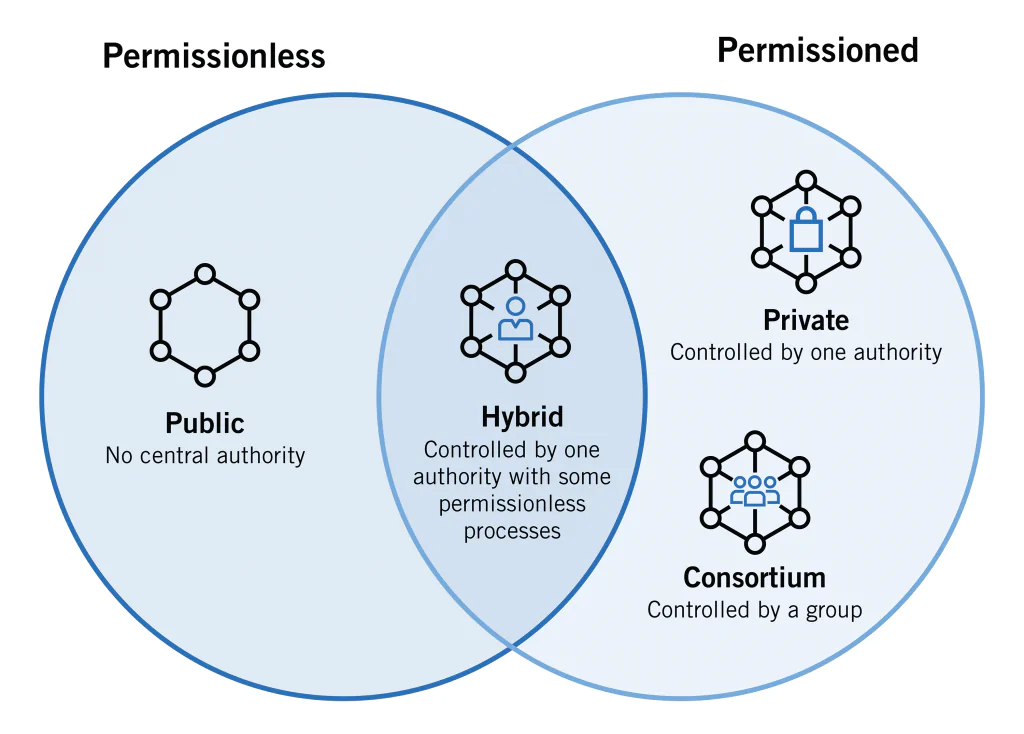
Blockchain Types
Blockchain technology has evolved by leaps and bounds over the last 10 years and the powerful capacity for innovation in data documentation and storage procedures has not gone unnoticed by governments and private companies. That is why they have also wanted to implement private blockchain networks (with restricted access).
We are going to go over the different types of blockchains that exist in relation to where it runs and who has access to it.
public blockchain
These are the best known examples such as Bitcoin and Ethereum. Being public means that they are accessible to any user in the world (they only need a computer and an internet connection). The counterpart of a public blockchain is its security management, since the greater the number of users, the higher the level of security we will need. This is where the consensus protocols and security measures that we will see later come into play.
private blockchain
Private blockchains are characterized by the fact that, unlike public ones, access to it depends on a central unit (company, organization or individual). The elements are the same as in a public blockchain. One of the best known examples of private blockchains is the Hyperledger network.
When a blockchain network is private (not public access) but its access and control is in the hands of a group of companies/individuals it is known as a blockchain consortium .
In the following image we see the different types of blockchain that we have discussed in a Venn diagram where we see how they are categorized according to the level of privacy.
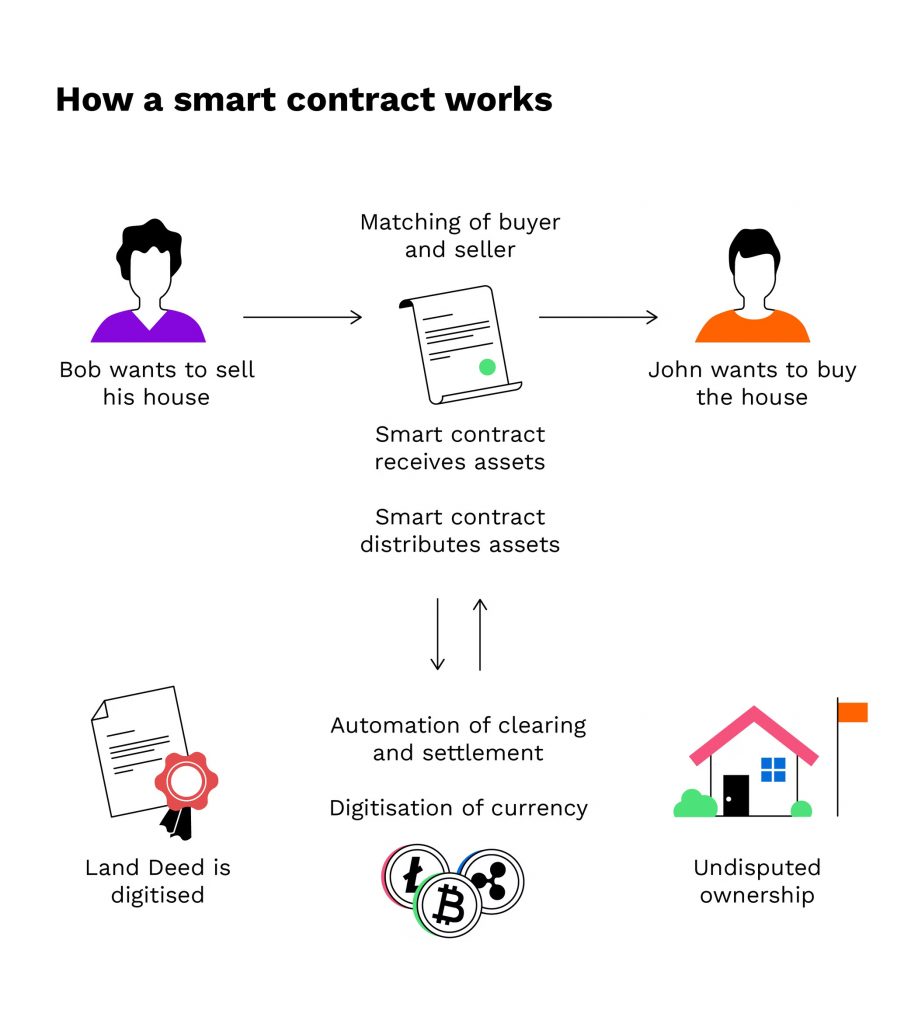
What are Smart Contracts
One of the advantages of 2nd generation blockchains like Ethereum is that they are programmable blockchains , that is, they allow us to host “instructions” or programs in the blockchains to execute a series of instructions if certain conditions are met.
These programs are known as smart contracts or smart contracts . For example, we can host a contract in which the distribution of an inheritance is automated once the condition of the death of the owner and issuer of said contract has been met.
Consensus protocols and nodes in Blockchain
One of the biggest challenges of these distributed networks is that they are widely susceptible to hacks and attempts to sabotage the block chains to introduce false transaction data (imagine being able to enter the central server of a bank and be able to modify the balance of the different customer accounts). To avoid all this type of problem there are multiple security measures and among them we find the consensus protocols.
A consensus protocol is a mechanism that allows regulating the way in which the nodes approve the blocks simultaneously so that they become part of the block chain.
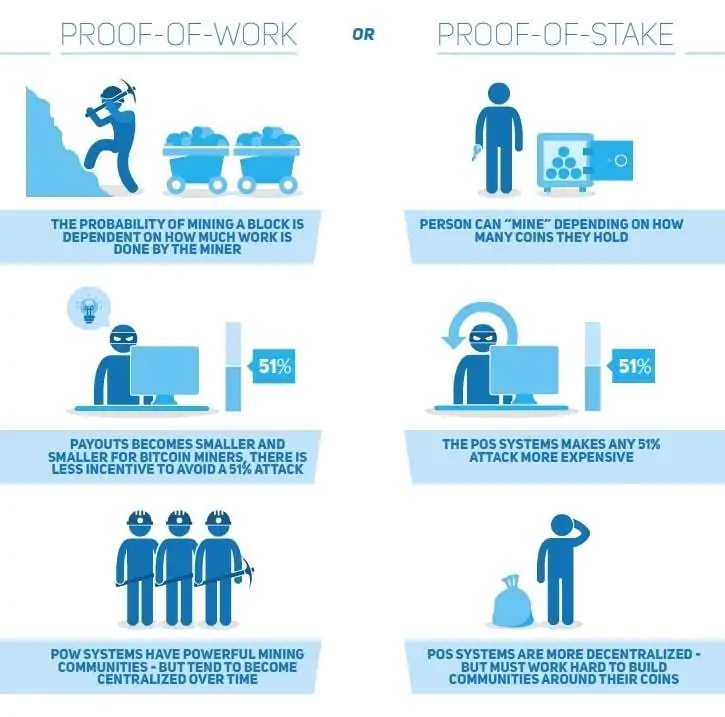
The main consensus protocols that exist are Proof of Work or **Proof of Work and Proof of Stake **or Proof of Participation . The Proof of History consensus protocol executed by the Solana blockchain has recently entered the market.
Proof of Work or Proof of Work (PoW)
This is the oldest consensus protocol that was first implemented on the Bitcoin Blockchain. In this protocol, all the nodes of the network are equal to each other and have to compete with the rest in order to receive the reward for validating the block.
In order to be the winning node, it has to solve a mathematical test of variable complexity (the more nodes that want to validate, the more difficult it will be) and therefore the one that has a greater computing capacity will have a greater probability of being the winning node.
The disadvantages of this consensus protocol are energy consumption (since there is direct competition between the various validators, all of them try to have the maximum number of “computers” to be able to process transactions) and **vulnerability ** (if a validator gets hold of 51% of the computing power of a network will have control of it as it will be able to validate even blocks with false or malicious information).
Proof of Stake or Proof of Stake (PoS)
In view of the inconveniences that the workforce protocol or PoW presents, a proof of participation or Proof of Stake protocol was designed.
In this protocol, in order for a specific block to be validated, the validator must have part of the native cryptocurrencies or tokens of the network in which it is trying to validate .
The algorithm will then randomly choose the validator that will add the next block, among all those who have purchased funds and deposited them in the node it is running. We could say that it works like a raffle: the more entries you have bought, the more likely it is that you can win validation and be the winning node.
The advantages of this protocol are that they are much faster, consume less energy and do not require such a strong investment in mining hardware as the PoW or Proof of Work protocol.
Differences between Bitcoin and Blockchain
For those who do not know the world of these technologies in depth, the difference between Blockchain and Bitcoin can be confusing at first and even be able to talk about the two interchangeably when it is not.
Blockchain is the decentralized technology that allows information to be stored in the form of blocks of data that are then arranged in a chain of blocks (hence the name).
A cryptocurrency is one of the most recognized ways to implement a blockchain network (a decentralized network that records transactions) and the most well-known example of a cryptocurrency is Bitcoin.
If you want more information about cryptocurrencies, we leave you this post about the largest cryptocurrencies by market capitalization.
Blockchain Advantages and Disadvantages
Another of its reasons for being is to reduce fraud in operations. All participants have access to the transactions and a consensus of all is needed to modify them. This builds trust in business , something that until now has been difficult to achieve online. Also, being a public trading blockchain protects the security of transactions as everyone has access to a single, shared source of trust.
One of the facilities that Blockchain provides is being able to carry out an economic transaction from Spain to any country in a time of between five and ten minutes. But it can also be applied, for example, to finance “stock” movements or sign smart contracts.
Blockchain Examples
1# Blockchain and its application in the financial sector
This technology is already being applied in many sectors, but those who are currently exploiting it the most are banks. Several studies confirmed at the time that 15% of banks and 14% of financial institutions plan to introduce Blockchain solutions and technologies in 2017. And it is expected that by 2020, 20% of global companies will integrate this technology . In reality, what banks are pursuing is to implement technologies to be able to eliminate intermediaries and distrust in transactions.
BBVA , Bankinter or Banco Santander are some of the big banks that have detected an important source of investment in Blockchain technology. They are beginning to install this system in their transactions, with the aim of improving the security of the processes and eliminating the costs involved in traditional transactions.
Blockchain reaches SMEs
Small and medium-sized companies represent close to 75% of all the companies that make up the Spanish economy, according to data from the 2015 ePyme Report: sectoral analysis of the implementation of ICT in Spanish companies . This data shows that SMEs are a fundamental pillar of the financial industry in our country, so all the technological innovations they develop will have a key impact on the current economic model.
The report Thermometer of the middle market in Spain reveals that 85% of entrepreneurs assure that the turnover of their companies will increase and only 2% believe that sales will decrease. This happens, among other factors, because SMEs have detected the need to go through a digital transformation process and, therefore, to investigate ways to open new business models adapted to the digital age.
Some startups are leading the introduction of Blockchain technology. They use it as a method to decentralize and let users control their own movements, without the need for third-party intervention.
For example, Storj is a startup that has developed a beta version of a service that allows you to create a decentralized database , using Blockchain technology, to increase security. To understand it, it would be like cloud storage services, such as Dropbox or Google Drive, but, unlike them, in this case there is no single provider that is responsible for the data that is stored.
Another possibility that Blockchain offers is the creation of Smart Contracts . It consists of automating business processes (payments, suppliers, supply…) through a virtual machine that stores and manages information. The machine becomes the person who talks to the suppliers and makes the payments. The Spanish startup Clluc creates platforms for companies to have access to these Smart Contracts .